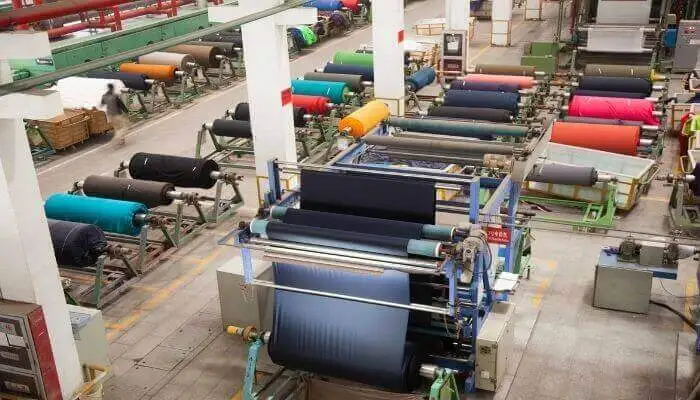
Do you ever find yourself lying awake at night, haunted by the ghost of textile industry’s significant sustainable production environmental footprint? Trust me, I’ve spent quite a few nights wrestling with those same fears.
My concern spiked when I learned that untreated wastewater from textile mills can directly contaminate our precious water sources. But don’t despair – in this blog post, we’re going to dive into sustainable production processes in the textile industry – processes that are not only viable but also hold tremendous potential for reducing environmental harm.
So, how about we buckle up and embark on this eco-journey together? Let’s explore greener practices for fabric manufacturing and work towards a future where sleep comes easy again!
Key Takeaways
- Sustainable textile production is an eco – friendly way of making clothes that reduces harm to the environment and people.
- By using organic cotton, hemp, and flax fibers, the textile industry can promote sustainability and reduce water usage and chemical dependency.
- Recycling and upcycling post – consumer textiles are important practices that help minimize waste, conserve resources like water and energy, and contribute to a cleaner environment.
Definition and Importance of Sustainable Textile Production
Sustainable textile production is an ecofriendly way to make clothes. It means less harm to the earth and its people. We use earth-friendly materials and cut down on water and energy use.
This helps fight pollution which harms our world a lot, especially from dirty water left over after making textiles.
In some parts of the world, clean water turns dirty because of this industry. But, when we look after how we make textiles, we can save more clean water. This helps us all live better lives in a healthier world.
So if you think about it, sustainable practices in this field are very important for everyone!
Historical Background and Evolution of Sustainable Practices in Textile Production
Long ago, textile making was not kind to our Earth. It used a lot of water and made a lot of trash. Over time, people in the industry saw this problem. They knew they had to change their ways.
Now, we work hard on saving water and energy in textile production. We also put less waste into the world. One way we do this is by reusing old clothes and turning them into new ones! This helps us keep useful parts from turning into waste.
We even figured out how to take back sodium hydroxide in a step called mercerization! Plus, thanks to things like EVAC vacuum suction systems, chemicals are not lost during dyeing anymore either!
Sustainable Fiber Production

We are making new fibers in a better way now. We get some fibers from plants like cotton. Cotton is safe for the earth and good to use again. It does not need much water or bad stuff to grow it.
We also make sure that growing cotton is good for people too.
Another type of fiber comes from hemp and flax plants. These kinds of plants are really tough but they still feel soft when you wear them as clothes! They don’t hurt the planet because they use less water and no bad things to grow!
Organic Cotton
Organic cotton is a type of cotton that is grown using sustainable farming practices. It promotes eco-friendly textiles and helps to conserve water. By choosing organic cotton, we can support the health of farmers and workers in the textile industry.
Organic cotton cultivation also helps to preserve biodiversity and maintain healthy soil. In addition, it is a greener alternative to conventional cotton, making it a great choice for those who care about the environment.
Cultivation and Growth Practices
Cultivation and growth practices in the textile industry are important for sustainable production. Here are some key practices to consider:
- Organic Cotton: Growing cotton without synthetic pesticides or fertilizers helps protect the environment and the health of farmers.
- Sustainable Cultivation Techniques: Implementing practices like crop rotation, companion planting, and natural pest control minimizes environmental impact.
- Water Conservation: Using drip irrigation systems and rainwater harvesting reduces water usage in textile farming.
- Eco-friendly Dyes: Choosing natural dyes or low-impact dyes limits chemical pollution in textile production.
- Regenerative Agriculture: Adopting regenerative farming methods helps restore soil health, increase carbon sequestration, and enhance biodiversity.
Environmental and Social Benefits
Optimizing textile production processes can bring about significant environmental and social benefits. By implementing sustainable practices, such as water conservation and energy efficiency measures, the textile industry can reduce its overall impact on the environment.
This includes reducing water consumption, minimizing chemical usage, and controlling pollution. Additionally, by adopting organic materials like organic cotton and silk, the industry can improve sustainability and promote healthier working conditions for workers involved in cultivation and manufacturing processes.
These efforts not only help protect our planet but also contribute to a more socially responsible supply chain that values worker well-being and promotes fair labor practices.
Hemp and Flax Fibers
In sustainable textile production, hemp and flax fibers play a vital role. These natural fibers offer eco-friendly alternatives to conventional materials, helping to reduce water usage and chemical dependency in the industry.
To further enhance sustainability, innovative processes are being developed for producing hemp and flax fibers. Nonconventional optimization methods like metaheuristics and genetic algorithms are being applied to improve efficiency and minimize pollution.
Additionally, advanced treatments such as enzymatic treatments, ultrasonic technology, and plasma treatment are being used to enhance fiber quality and performance while reducing environmental impact.
Recycled and Upcycled Fibers

Recycled and upcycled fibers play a crucial role in sustainable textile production. These fibers are made from post-consumer textiles that have been collected, sorted, and processed to create new materials.
By recycling these textiles, we can reduce waste and minimize the environmental impact of the textile industry.
When we recycle textiles, we help conserve resources like water and energy. By reusing materials instead of producing new ones, we can significantly reduce water consumption in the production process.
This is important because textile production is known for its high water usage. Moreover, recycling also reduces energy consumption by avoiding the need to extract raw materials and manufacture new fibers.
Upcycling is another innovative technique that transforms discarded textiles into new products with higher value. Instead of being thrown away or recycled into basic fibers, upcycling allows us to repurpose these materials into something unique and desirable.
This not only reduces waste but also gives old garments a second life.
Recycled and upcycled fibers are gaining popularity among consumers who prefer environmentally friendly products. By incorporating these fibers into their collections, brands can offer sustainable options without compromising on quality or style.
As more people become aware of the importance of sustainability, demand for recycled and upcycled textiles continues to grow.
By embracing recycled and upcycled fibers in our textile production processes, we can contribute to a more sustainable future while satisfying customer preferences for eco-friendly goods.
Recycling of Post-Consumer Textiles
Recycling post-consumer textiles is an essential practice for promoting sustainable production in the textile industry. Textile waste, such as old clothing and fabric scraps, often ends up in landfills, contributing to environmental pollution.
By collecting and sorting these textiles, they can be processed and transformed into new fibers or products through recycling or upcycling techniques. This helps reduce the demand for virgin materials and minimizes the environmental impact of textile production.
Additionally, recycling post-consumer textiles supports the concept of circular economy, where resources are reused instead of discarded. By implementing effective recycling practices, we can contribute to a cleaner environment and a more sustainable fashion industry while conserving valuable resources like water and energy.
Collection and Sorting
Collection and sorting are important steps in exploring sustainable production processes in the textile industry. By effectively managing waste, we can reduce our environmental impact and promote a circular economy. Here are some key points about collection and sorting:
- Textile waste can be categorized into liquids, solids, and gases. Proper collection and sorting ensure that each type of waste is handled appropriately.
- Recycling plays a crucial role in sustainable production. By collecting post – consumer textiles, we can prevent them from ending up in landfills and instead transform them into new materials.
- Sorting involves categorizing textiles based on their composition, color, and condition. This allows for efficient recycling and upcycling processes.
- Advanced technologies such as automated sorting systems use sensors to identify different types of textiles, making the process faster and more accurate.
- Collection programs can be implemented at various levels, including individual households, businesses, and collaboration with retail stores or non-profit organizations.
Processing and Fiber Creation
In sustainable textile production, the processing and creation of fibers play a vital role. There are various methods and technologies that contribute to reducing the environmental impact in this stage. Here are some important facts about processing and fiber creation:
- Enzymatic treatments: Enzymes are used to modify fibers, improve their properties, and reduce the need for harsh chemicals. This helps minimize pollution and waste.
- Ultrasonic treatments: Ultrasonic waves help in the dyeing process by enhancing the penetration of dyes into fibers, resulting in reduced water consumption and chemical usage.
- Foam technology: Foam dyeing techniques use less water and energy compared to traditional dyeing processes. This innovative method also allows for better color uniformity on textiles.
- Recycling: Recycling post-consumer textiles can contribute to sustainable fiber creation. By collecting and sorting discarded textiles, useful materials can be recovered and transformed into new fibers.
- Recovery of useful materials: The textile industry generates different types of waste, including liquids, solids, and gases. These waste materials offer opportunities for recycling and recovering valuable resources.
- Energy consumption: Energy usage in textile production is mainly driven by heating process water and laundering after consumer use. Implementing energy-efficient equipment and practices can help reduce energy consumption significantly.
Upcycling Techniques
Upcycling techniques play a significant role in sustainable textile production. These methods involve transforming discarded textiles into new and useful products, reducing waste and environmental impact.
One example is the recovery and recycling of PVA size, a chemical used in textile sizing. The use of ultrafiltration (UF) reverse osmosis technology has been effective for over 40 years in this process.
Additionally, vacuum flash evaporation (VFE) is a promising new technology for PVA size recovery. By implementing upcycling techniques, the textile industry can save energy and water while minimizing waste generation.
Transformation of Discarded Textiles
Transforming discarded textiles is a crucial step towards sustainable production in the textile industry. Textile waste, if not properly managed, can contribute to environmental pollution.
Untreated wastewater from textile factories often contains hazardous substances that can harm ecosystems and human health. However, through optimization techniques and the application of best available techniques (BAT), we can minimize these negative impacts.
By recycling and reusing discarded textiles, we reduce the need for new production and save resources. Innovative upcycling methods are being developed to transform waste materials into new products with added value.
Innovative Upcycling Methods
Innovative upcycling methods are a way to reduce waste and environmental pollution in the textile industry. By transforming discarded products or waste materials into new, higher-value items, we can give them a new life and purpose.
For example, we can repurpose textile scraps to make unique accessories or turn old garments into insulation materials. These innovative methods help decrease the demand for raw materials, conserve resources, save energy, and minimize waste generated during textile production.
Some companies even offer customers the option to return old garments for recycling or upcycling purposes as part of their commitment to sustainable fashion and circular economy principles.
Water and Energy Efficiency in Textile Production
Water and energy efficiency are crucial aspects of sustainable textile production. The textile industry uses a large amount of water in its production processes, resulting in environmental pollution.
Untreated wastewater from the industry contains hazardous substances that can contaminate clean water sources. This is especially problematic in underdeveloped and developing countries where wastewater treatment is limited due to high costs.
To address this issue, it is important to optimize textile production processes to reduce both water and chemical usage. By doing so, we can promote more sustainable production practices while also reducing costs associated with wastewater treatment.
Water Management
Water management is a crucial aspect of sustainable textile production. The textile industry uses a lot of water, which can lead to environmental pollution. Untreated wastewater contains hazardous substances that can harm clean water sources.
To address this problem, it is important to reduce the cost of treating wastewater. Optimization of textile production processes can help minimize water usage and chemical consumption, resulting in more sustainable production methods.
Innovative approaches like metaheuristics and genetic algorithms are being explored to make textile processes more environmentally friendly and reduce pollution.
Water Recycling and Treatment
Water recycling and treatment are crucial steps in achieving sustainable production processes in the textile industry. Here are some key points to consider:
- High water consumption: The textile industry is known for its significant water usage during manufacturing processes, leading to water scarcity issues.
- Environmental pollution: Wastewater from textile production often contains pollutants, such as dyes and chemicals, which can harm ecosystems if not treated properly.
- Importance of recycling: Implementing water recycling systems allows textile manufacturers to reuse and treat wastewater, reducing the strain on freshwater resources.
- Advanced treatment technologies: Utilizing advanced water treatment technologies can effectively remove contaminants from wastewater, ensuring that it meets regulatory standards before being discharged or reused.
- Resource efficiency: Recycling wastewater reduces the need for fresh water intake, conserving this valuable resource and minimizing environmental impact.
- Green practices: Incorporating eco-friendly production methods, such as implementing closed-loop systems and adopting sustainable dyeing techniques, further enhances water conservation efforts in the textile industry.
Water Reduction Techniques
Water reduction techniques are essential in the textile industry to minimize water consumption and reduce environmental impact. Here are some effective methods used in sustainable textile production:
- Adopting closed-loop systems: Implementing closed-loop systems allows for the recycling and reuse of water throughout the production process, reducing overall water consumption.
- Implementing low-water dyeing processes: Using innovative dyeing techniques such as air dyeing or cold pad batch dyeing can significantly reduce water usage compared to traditional methods.
- Embracing enzymatic treatments: Enzymes can be used in various stages of textile production, such as desizing, scouring, and bleaching, to achieve the desired results with lower water requirements.
- Utilizing ultrasonic technology: Ultrasonic treatments can enhance fabric finishing processes by reducing the need for excessive rinsing, resulting in significant water savings.
- Implementing advanced fiber pre-treatment: Advanced pre-treatment technologies like plasma treatment or ozone washing can improve fabric properties without the need for extensive washing, thus conserving water resources.
Energy Efficiency
Improving energy efficiency is crucial for sustainable textile production. By optimizing production processes, we can reduce energy consumption and minimize our carbon footprint. Implementing Best Available Techniques (BAT) measures in textile mills has been proven to lower energy usage.
In the textile industry, heating process water and laundering after consumer use are the main drivers of energy consumption. Adopting sustainable practices like using greener materials and organic fibers can contribute to improved energy efficiency in textile processing.
Embracing renewable energy sources and implementing energy reduction strategies will help us become more environmentally responsible while ensuring a green and sustainable future.
Use of Renewable Energy
Renewable energy sources are a key part of sustainable production processes in the textile industry. By harnessing green technology and using clean, renewable resources like solar and wind power, we can reduce our carbon footprint and minimize our environmental impact.
Implementing energy-efficient practices and equipment, such as using energy from solar panels or wind turbines to power textile mills, can significantly decrease energy consumption.
This not only helps conserve valuable resources but also improves product quality while promoting sustainable development. By embracing eco-friendly practices like utilizing renewable energy sources, the textile industry in the United States can move towards greater sustainability and contribute to a cleaner and greener future for all.
Energy-Efficient Equipment and Processes
In sustainable textile production, energy-efficient equipment and processes play a crucial role in reducing the environmental impact of manufacturing. By using advanced technologies and optimizing processes, we can conserve energy, reduce carbon footprint, and save costs.
Implementing best available techniques (BAT) recommended by the European Council helps textile mills reduce water and energy consumption as well as CO2 emissions. Nonconventional optimization methods like metaheuristics and genetic algorithms are being applied to improve sustainability further.
Enzymatic treatments, ultrasonic treatments, and plasma technology are also used for eco-friendly textile processing. Investing in energy-efficient equipment not only benefits the environment but also leads to cost savings while maintaining product quality.
Waste Reduction and Circular Economy
In the textile industry, waste reduction and embracing a circular economy are crucial for sustainability. I have discovered that the textile industry is a major contributor to environmental pollution.
To tackle this issue, implementing waste management strategies is essential. By minimizing waste in production and reusing or recycling production waste, we can reduce our impact on the environment.
To further promote sustainability, designing products for durability and repurposing is important. This means creating textiles that last longer and can be easily transformed into new products at the end of their lifecycle.
Additionally, practicing extended producer responsibility (EPR) encourages manufacturers to take responsibility for their products throughout their entire lifecycle.
Embracing a circular economy also plays a significant role in reducing waste. Instead of using resources once and discarding them, we should aim to keep materials circulating within the economy by recycling or upcycling them into new products.
By doing so, we can minimize our reliance on raw materials and decrease environmental degradation.
It’s worth mentioning that these efforts are not only beneficial for the environment but also make economic sense. By reducing waste, companies can save money on raw materials and disposal costs while also attracting environmentally conscious consumers.
To sum it up briefly: Waste reduction measures such as minimizing waste in production processes and adopting circular economy principles are vital steps towards achieving sustainability in the textile industry.”
Waste Management
Waste management is a crucial aspect of sustainable textile production. The textile industry generates a lot of waste, which can contribute to environmental pollution if not handled properly.
This waste includes things like leftover fabric scraps, dye chemicals, and packaging materials. To address this issue, companies are focusing on minimizing waste in production processes.
They are finding ways to reuse and recycle materials instead of throwing them away.
One important step in waste management is proper sorting and disposal of different types of waste. For example, fabric scraps can be collected and recycled into new yarn or used for insulation.
Hazardous substances from dyes need to be treated carefully to prevent water contamination. Some companies also use innovative methods like transforming discarded textiles into new products through upcycling.
Another aspect of waste management is the implementation of circular economy principles. Instead of following a linear model where products are made, used, and then thrown away, the circular economy aims to keep resources in use for as long as possible by promoting recycling and repurposing.
Minimizing Waste in Production
Minimizing waste in production is crucial for sustainable textile production. Here are some important steps that can be taken:
- Adopting lean manufacturing practices to identify and eliminate waste throughout the production process.
- Implementing efficient inventory management systems to reduce excess raw materials and finished goods.
- Using cutting – edge technology, such as automated cutting machines, to optimize fabric utilization and minimize material waste.
- Recycling and reusing textile scraps and offcuts instead of discarding them, reducing landfill waste.
- Encouraging collaboration with suppliers to develop packaging solutions that are eco-friendly and minimize waste.
- Conducting regular audits to identify areas where waste can be reduced or eliminated altogether.
- Investing in employee training programs to raise awareness about waste reduction techniques and encourage innovative ideas.
Reusing and Recycling Production Waste
In sustainable textile production, reusing and recycling production waste is crucial. Here are some important practices and technologies:
- Industrial waste management: Proper management of various categories of industrial waste, such as liquids, solids, and gases, is essential for minimizing environmental impact.
- Recycling and recovery: Technologies like sodium hydroxide recovery during the mercerization process can recover up to 90% of this chemical, reducing waste and resource consumption.
- EVAC vacuum suction system: This system helps recover hot alkaline hydrogen peroxide, additives, and finishing chemicals in the textile dyeing process, preventing their release into the environment.
- Desizing effluent: Effluents containing Polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) from desizing processes can have a high chemical oxygen demand (COD), posing risks to water bodies. Proper treatment and recycling methods should be employed to minimize harm.
- Vacuum flash evaporation (VFE): VFE technology has been proposed for the recovery and recycling of PVA size in textile production. It offers potential reductions in energy and water consumption compared to traditional methods like ultrafiltration.
Circular Economy Principles
Circular economy principles play a crucial role in promoting sustainable production processes in the textile industry. These principles emphasize resource efficiency, waste reduction, and recycling to minimize the environmental impact of manufacturing textiles.
By adopting circular economy practices, such as reusing materials, designing for durability and repurposing, and implementing extended producer responsibility (EPR), the textile industry can reduce its reliance on virgin resources and minimize pollution.
This shift towards a circular economy not only helps conserve natural resources but also supports sustainable development by creating a more eco-friendly and efficient production system.
Design for Durability and Repurposing
Designing textiles with durability and repurposing in mind is a crucial aspect of sustainable production processes in the textile industry. By creating products that are built to last, we can reduce the need for frequent replacements and minimize waste.
When textiles are made with high-quality materials and strong construction techniques, they are more likely to withstand daily wear and tear, extending their lifespan. This not only benefits consumers by providing them with products that will last longer but also reduces the environmental impact associated with producing new items.
Additionally, designing for repurposing allows textiles to have multiple uses throughout their lifecycle. For example, garments can be designed in a way that makes it easy to alter or transform them into new styles or accessories, allowing them to be enjoyed for even longer periods of time.
Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR)
As a responsible producer of textile products, it is important to understand the concept of Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR). EPR legislation holds producers accountable for the environmental impacts of their products throughout their lifecycle.
This means that producers are responsible for managing and financing the collection, sorting, recycling, and disposal of textile products at the end of their life cycle.
EPR aims to incentivize producers to implement sustainable design and production processes in order to reduce waste and pollution. In the European Union (EU), EPR legislation currently applies to household textiles and is expected to be extended to the furniture industry as well.
Upholstery textiles can be subject to EPR through legal obligations or voluntary schemes.
Sustainable Supply Chains and Fair Labor Practices
In the textile industry, it is important to have sustainable supply chains and fair labor practices. This means that companies need to be transparent about where their materials come from and how they are produced.
It also means ensuring that workers are treated well and paid fair wages. By having sustainable supply chains, we can reduce the environmental footprint of textile production and support ethical practices.
One way to achieve sustainable supply chains is by traceability of materials. This means being able to track where the fibers and fabrics used in textiles come from, ensuring that they meet certain environmental and social standards.
Additionally, companies should prioritize fair labor practices by providing safe working conditions, reasonable hours, and fair wages for all workers involved in the production process.
By implementing these measures, we can create a more environmentally-friendly textile industry while also supporting the rights and well-being of workers. It is important for both consumers and companies to push for sustainable supply chains and fair labor practices in order to make a positive impact on our environment and society overall.
Supply Chain Transparency
Supply chain transparency is an important aspect of sustainable production processes in the textile industry. It involves being able to trace and see where materials come from, ensuring ethical sourcing and reducing the environmental impact of textile manufacturing.
By implementing practices like Best Available Techniques (BAT) and nonconventional optimization methods, companies can improve supply chain transparency. This includes utilizing technologies like metaheuristics and genetic algorithms to enhance sustainability.
Additionally, using sustainable production practices such as enzymatic treatments and advanced fiber pre-treatment can also contribute to better supply chain transparency in the textile industry.
Traceability of Materials
Traceability of materials is a crucial aspect of sustainable production in the textile industry. It helps ensure that the materials used in textile production are sourced responsibly and ethically.
By implementing traceability measures, we can reduce the environmental impact of textile production by identifying and addressing issues such as water consumption and pollutant content.
In fact, the European Council’s Best Available Techniques (BAT) framework recognizes traceability as a method to minimize environmental harm in this industry. Moreover, traceability also improves product quality and meets customer preferences for sustainable and environmentally friendly goods.
Fair Labor Practices
Fair labor practices play a crucial role in exploring sustainable production processes in the textile industry. It involves ensuring ethical labor practices, protecting worker rights, and promoting socially responsible production.
By prioritizing fair wages and working conditions, preventing worker exploitation, and embracing responsible sourcing, the textile industry can contribute to a more sustainable manufacturing sector.
Companies need to prioritize human rights in their supply chains and adopt fair trade standards to create a positive impact on workers’ well-being while demonstrating corporate social responsibility.
Worker’s Rights and Well-being
As a worker in the textile industry, I understand the importance of labor rights and well-being. It is crucial for companies to prioritize the health and safety of their employees.
Unfortunately, unsustainable production processes can have negative impacts on workers’ rights and well-being. For instance, the high water and energy consumption in textile production can lead to environmental pollution, which affects both air quality and water sources.
This pollution can expose workers to hazardous substances that pose risks to their health. Additionally, the use of toxic chemicals in textile manufacturing can also have adverse effects on workers’ well-being.
Fair Wages and Working Conditions
Ensuring fair wages and working conditions is crucial for sustainable textile production. It’s not just about being ethical; it’s also about our social responsibility. When workers are paid fair wages, it improves their livelihoods and allows them to contribute positively to their communities.
Providing safe and healthy working conditions is important too, as it prevents accidents and keeps workers safe. Fair wages and good working conditions also lead to higher employee satisfaction and productivity, which in turn improves the overall performance of textile companies.
By prioritizing fair wages and working conditions, we can create a more sustainable industry that benefits everyone involved.
Certifications and Standards in Sustainable Textile Production
Certifications and standards are important in promoting sustainable textile production in the industry. They help ensure that textile manufacturers follow environmentally friendly practices and meet specific criteria for sustainability.
One well-known certification is the Global Organic Textile Standard (GOTS), which verifies that textiles are produced using organic fibers and have minimal environmental impact. Another important certification is Cradle to Cradle Certified™, which evaluates products based on their material health, recyclability, renewable energy use, water stewardship, and social fairness.
The bluesign® System also sets strict criteria for environmentally friendly textile production by focusing on resource productivity, consumer safety, air emission reduction, and occupational health and safety.
Fair Trade Certification ensures fair wages and good working conditions for employees involved in the production of textiles.
These certifications not only help consumers make more informed choices but also encourage textile manufacturers to adopt sustainable practices throughout their supply chains. By adhering to these standards, companies can reduce their environmental impact by minimizing water consumption, energy usage, CO2 emissions while improving product quality.
Sustainable manufacturing not only benefits the environment but also satisfies customer preferences for eco-friendly products.
Global Organic Textile Standard (GOTS)
The Global Organic Textile Standard (GOTS) is a widely recognized standard for organic textiles. It covers the entire supply chain of textile production, from the cultivation of raw materials to the labeling and packaging of finished products.
GOTS-certified textiles must contain a minimum of 70% organic fibers, ensuring that they are made with eco-friendly and sustainable materials. One key aspect of GOTS is its prohibition on the use of toxic substances in textile production, which helps protect both consumer health and environmental well-being.
Additionally, GOTS promotes transparency and traceability in the textile supply chain, allowing consumers to make informed choices about their purchases. Overall, GOTS certification ensures that textiles meet strict standards for sustainability, nontoxicity, and ethical production practices.
Cradle to Cradle Certified™
Cradle to Cradle Certified™ is an important certification for the textile industry. It ensures that products are made in a sustainable way, from materials sourcing to manufacturing and even recycling.
This certification promotes the use of renewable energy, water conservation, and waste reduction throughout the production process. It also considers factors like worker safety and fair labor practices.
With Cradle to Cradle Certified™ textiles, we can trust that our clothes are environmentally friendly and ethically produced.
bluesign® System
The bluesign® System is an important certification program that focuses on reducing the environmental impact of textile production. As part of this system, manufacturers are guided in using safe chemicals and ensuring water conservation, energy efficiency, waste reduction, and emission control.
By implementing the bluesign® System, textile manufacturers can significantly decrease their environmental footprint while also improving the sustainability of their production processes.
Fair Trade Certification
Fair Trade Certification plays a crucial role in sustainable textile production. By implementing Fair Trade measures, textile mills can reduce water and energy consumption, as well as CO2 emissions.
This certification also helps improve product quality and meet the growing customer demand for environmentally friendly goods. Through Fair Trade practices, production costs can be minimized, while wastewater pollutants are reduced.
Fair Trade Certification is a solution that contributes to reducing the environmental impact of the textile industry and promoting fair labor practices.
In summary, Fair Trade Certification is an essential aspect of sustainable textile production in the United States. It not only helps conserve resources like water and energy but also improves product quality and meets customer demands for eco-friendly products.
Technological Innovations in Sustainable Textile Production
Technological innovations play a crucial role in making textile production more sustainable. These advancements help reduce the environmental impact by minimizing waste, conserving water, and reducing pollution.
One such innovation is 3D weaving and printing, which allows for more efficient material usage and customization of designs. By using this technology, less fabric goes to waste during the production process.
Additionally, nanotechnology is being used in textile finishing to enhance performance and durability while reducing chemical usage. With these innovative approaches, the textile industry can make significant strides towards achieving eco-friendly production practices.
Overall tone: Informative
3D Weaving and Printing
I’m excited to share with you about 3D weaving and printing, two innovative processes that are revolutionizing the textile industry. These techniques have the potential to contribute significantly to sustainable production.
How? Well, let me explain.
Firstly, 3D weaving involves interlacing yarns together to create fabric structures in three dimensions. This method allows for intricate designs and patterns while reducing waste compared to traditional manufacturing methods.
By optimizing material usage, 3D weaving helps conserve resources and promotes sustainability.
Secondly, we have 3D printing, which uses additive manufacturing techniques to build up layers of material. This process enables precise customization and personalization in garment production.
Reduced Waste and Material Usage
Reducing waste and material usage is crucial for sustainable textile production. By implementing efficient production processes, we can minimize the amount of waste generated and reduce our reliance on raw materials.
This not only helps protect the environment but also saves resources and lowers production costs. Techniques such as recycling, upcycling, and redesigning products can help us make the most of existing materials, decreasing the need for new ones.
Additionally, optimizing manufacturing processes can help minimize fabric scraps and cut down on chemical usage. By adopting these sustainable practices in the textile industry, we can create a more eco-friendly future by conserving resources while still meeting consumer demands.
Customization and Design Advancements
In the textile industry, there is a growing focus on customization and design advancements to promote sustainable production processes. This means creating personalized products that meet individual preferences while also considering environmental responsibility.
By embracing innovative design techniques and manufacturing methods, the industry aims to minimize water consumption, reduce energy usage, and decrease waste generation. Enzyme technology is being explored as a more sustainable option for textile processing, replacing traditional chemical processes with enzymes that are biodegradable and less harmful to the environment.
Additionally, natural colorants derived from plants, animals, and minerals are gaining popularity as eco-friendly alternatives to synthetic dyes. Enhancing supply chain visibility allows for better traceability of materials, ensuring transparency and promoting sustainability throughout the entire production process.
Nanotechnology in Textile Finishing
Nanotechnology is a cutting-edge field that has exciting applications in the textile industry, particularly in finishing processes. By using nanotechnology, we can enhance the performance and durability of textiles while also reducing their environmental impact.
This innovative approach allows us to optimize textile treatments, making them more sustainable and eco-friendly. With nanotechnology, we can achieve advanced functionalities like water and stain repellency, increased strength, improved dye absorption, and even self-cleaning properties.
These advancements contribute to sustainable manufacturing practices by reducing waste and pollution in the textile industry. Through the use of nanotechnology in textile finishing, we are revolutionizing how textiles are produced while striving for a greener future.
Enhanced Performance and Durability
Optimizing textile production processes can enhance the performance and durability of textiles. By reducing water usage and minimizing chemical usage, we can create eco-friendly and sustainable practices.
Implementing Best Available Techniques (BAT) measures in textile mills has been shown to improve product quality, resulting in customer satisfaction for environmentally friendly goods.
Enzymatic treatments, ultrasonic treatments, and advanced fiber pre-treatment are some examples of sustainable production practices that can enhance performance and durability in the textile industry.
Reduced Environmental Impact
Reducing environmental impact is crucial in the textile industry. Textile production processes contribute significantly to pollution, particularly through high water consumption and pollutants in wastewater.
This untreated wastewater contains hazardous substances that pollute clean water sources. To address this issue, we need to focus on reducing the cost of wastewater treatment. By optimizing textile production processes, we can minimize water and chemical usage, leading to more sustainable and environmentally-friendly production methods.
FAQs
1. What is sustainable production in the textile industry?
Sustainable production in the textile industry refers to manufacturing processes that minimize negative environmental impacts and prioritize social responsibility.
2. Why is it important to explore sustainable production processes in the textile industry?
Exploring sustainable production processes in the textile industry is important because it helps reduce pollution, conserve resources, promote worker safety, and meet consumer demand for eco-friendly products.
3. What are some examples of sustainable production practices in the textile industry?
Examples of sustainable production practices in the textile industry include using organic or recycled materials, implementing water and energy-saving techniques, reducing chemical use, and ensuring fair working conditions.
4. How can companies transition to more sustainable production processes?
Companies can transition to more sustainable production processes by conducting audits to identify areas for improvement, investing in eco-friendly technology and machinery, collaborating with suppliers who share their sustainability goals, and educating employees on best practices.
5. What are the benefits of adopting sustainable production practices?
Adopting sustainable production practices in the textile industry can lead to reduced environmental impact, cost savings through resource efficiency, improved reputation among consumers who value sustainability, and a healthier work environment for employees.